

Homes and businesses installing a geothermal heat pump as a source of heating are becoming more and more popular. Currently, this trend is particularly popular in the southern and western parts of the United States; however there are still plenty of locations that are opting for geothermal. Although geothermal is extremely efficient and a “green” form of energy, there are still times when a traditional air-source heat pump may be a better option. The differences between the two are minor, but can make a big difference.
It may come as a surprise, but geothermal heating has been used in the United States for over 60 years. The unique way that geothermal works is that it uses heat from the earth which makes it clean and sustainable. The heat comes from hot water and hot rock a few miles under the surface of the earth. In some cases, it can be even deeper into molten rock. The easiest way to describe it is “geothermal springs for power plants.” The goal is to tap into hydrothermal convection. Cool water gets into Earth’s crust, is heated up, and then rises to the surface as steam. The steam is then captured and used for electric generators. A geothermal power plant will drill its own hole to easily capture more steam to generate more power. Alternatively, geothermal can be used directly to heat buildings without the use of a power plant.
Geothermal or ground-source heat pumps for homes are intended to replace your existing furnace and air conditioner. They use the natural heating and cooling properties of the earth. During the winter, when the ground is warmer than the air, a geothermal pump cycles this heat into your home. In the summer, the cool ground acts as a sink and absorbs warmth. Geothermal Heat pumps also require only a small amount of energy to operate — far less than it takes to run your furnace or A/C. By reducing your reliance on these energy-intensive appliances, you can save considerably without sacrificing your home comfort.
There is potential for geothermal to have a significant role in the United States going fully green for energy production. It is one of the only renewable sources that generate continuous power. Because of that, it can balance the variable energy sources of wind and solar. Geothermal power plants can easily change how much electricity they can generate to cover any deficit by wind and solar. Therefore, not supplying enough power to cover demand wouldn’t be an issue. Also, the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) has predicted that the leveled cost of energy for new geothermal plants (that will start “production” in 2019) will be less than both natural gas and coal plants. The cost being lower will give power companies an incentive to start creating geothermal plants instead of the alternative.
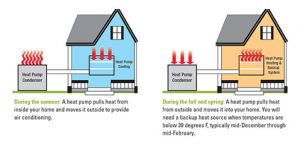
In simplest forms, a heat pump uses the same process as a refrigerator to keep its insides cool. It uses absolutely no fuel and instead uses refrigerator fluid to absorb exterior heat and transfers it where it needs to go by a system of fans. The process varies slightly depending on the season. In winter, air-source heat pumps transfer outside heat to the inside by using a system of coils that pull in the heat. In summer, the reverse happens and warm interior air is pushed to the outside. Air-source heat pumps are 45% and more efficient than standard AC units and conventional fuel-burning heating systems, respectively.
Traditional air-source heat pumps for homes can be installed as a complete stand-alone heating and cooling system, or they can replace your AC unit and work with a fossil fuel furnace. They consist of two major components: an outdoor unit that contains a fan and coil, and an indoor unit, also known as an air handler, that also has a fan and coil.
Air-source heat pumps also have a compressor that pressurizes refrigerant that rejects and absorbs heat as it moves through the system. A reversing valve can reverse the flow of the refrigerant, enabling the unit to change from heating to cooling and vice-versa. There’s also an expansion valve that regulates the refrigerant’s flow.
Most air-source heat pumps are an efficient method of heating your home when the outdoor temperature is above 25°F. Below this temperature, the performance levels are reduced and your home may require supplemental heat. A stand-alone system will require an auxiliary electric heat kit. If a home heat pump is installed to work with a furnace, the furnace will automatically provide the home’s heating needs once the outdoor temperature drops below 25°F.
Both geothermal and air-source heat pumps are extremely efficient. The difference between them is that geothermal uses water instead of air. Because of that, geothermal system do not have to move as much air to heat and cool and runs at 300% – 600% efficiency even in the coldest of temperatures. Alternatively, air-source heat pumps operate at 175% – 300% efficiency when it dips to very cold temperatures.
Geothermal has a much higher purchase and install cost, but long term, lower energy costs will easily recoup the investment. You are also eligible for a 30% federal tax credit if your geothermal system is Energy-star rated. Air-source heat pumps have a lower purchase and install cost and are much faster to install. Like geothermal, they reduce energy costs but not as significantly as geothermal. If the system is extremely efficient, you can get a tax credit of up to $300.
Unlike air-source heat pumps, geothermal systems are all underground or indoors. That makes them safe from the elements and any possible vandalism. They typically last approximately 25 years. Air-source heat pumps require regular cleaning and maintenance and are easily damaged and last around 15 years.
Deciding on which system is best for you may simply come down to how much room is available. If the area is small or has expensive landscaping, geothermal may not be a good fit as it requires extensive excavating. Air-source heat pumps are much smaller and do not require as much space.Geothermal and air-source heat pumps are excellent options when it comes to home heating. They are both extremely efficient compared to standard forms of heating and are relatively clean sources of energy. With either system, you know you’ll be making a great choice for an efficient, long term option to heat and cool your home.
Discover more about high-efficiency heat pumps here.